The human muscular system
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
The human muscular system is made up of over 600 muscles. The primary purpose of the muscular system is to enable our body movements. They make up the bulk of the body and form almost 1/3rd of the body weight. Blood vessels and nerves run to every muscle and control and regulate every muscle function.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Functions of the muscular system
- It helps us maintain posture and body position.
- It supports soft tissues and internal organs.
- It helps us maintain our body temperature.
- It enables all our voluntary movements like moving skeletal bones for body movements, like walking, running, chewing, playing the piano; and involuntary movements like breathing, beating of heart, moving food through the digestive system, blood through the circulatory system, and fluids through the excretory system.
Properties of muscles
- Excitability – Muscles are capable of receiving and responding to nervous stimulation.
- Contractibility – After receiving stimulation, muscles are capable of contracting or shortening.
- Extensibility – A muscle can be stretched to about three times their contracted length without rupturing.
- Elasticity – It is the ability of a muscle to recoil or bounce back to the muscle’s original length and shape after contraction and extension.
- Adaptability – The response of a muscle depends upon the kind of stimulus received. In simple words, a muscle will enlarge (hypertrophy) with increased work, as in bodybuilders or they may waste away (atrophy) due to immobility, malnutrition, or aging.

Hypertrophy

Atrophy
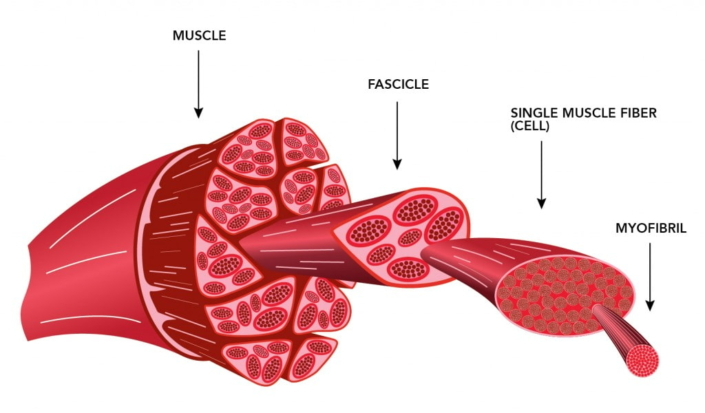
Composition of muscle tissues
Muscle tissues are soft tissues that comprise of elongated cells, also known as muscle fibers tightly bundled together. A bundle of skeletal muscle fibers is called a fascicle. A basic rod-like unit of a muscle fiber or cell is called myofibril that is composed of proteins like actin, myosin, titin etc. Each time the bundles receive signals from the nervous system, they contract causing a force and motion.
Personalized Online Tutoring from eTutorWorld
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE TRIAL Session.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Three types of muscle tissues
- Smooth muscles – Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles and constitute much of the musculature of internal organs and the digestive system. They contract slowly and automatically. They consist of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single centrally located nucleus. They are found within the walls of organs and structures like the alimentary canal, bronchi, urinary tract and blood vessels.
- Cardiac muscles – Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. They are not subject to voluntary control. The contractions of cardiac muscles are highly coordinated to pump blood into the circulatory system. Cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and usually contain one centrally located nucleus.
- Skeletal muscles – Skeletal muscles attach to bones and move them voluntarily in response to signals from the nervous system. Attached to the skeletal system, they provide the skeleton with the ability to move. They help us maintain posture. Each skeletal muscle is made up of hundreds of muscle fibers bundled together. Each skeletal muscle fiber is a single cylindrical muscle cell. Skeletal muscles have an abundant supply of blood vessels and nerves.
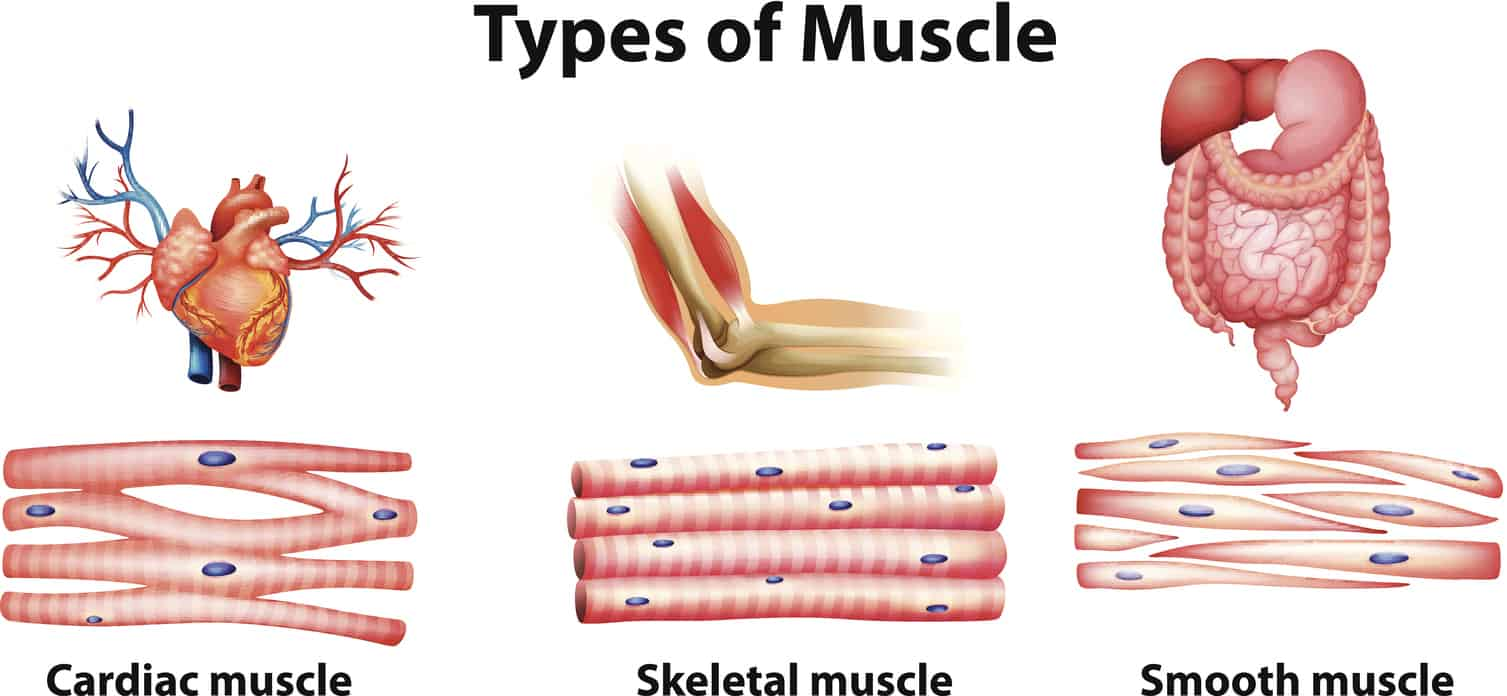
Notice the striations on cardiac and skeletal muscles. They are thus known as striated muscles as they are packed into highly regular arrangement of bundles.
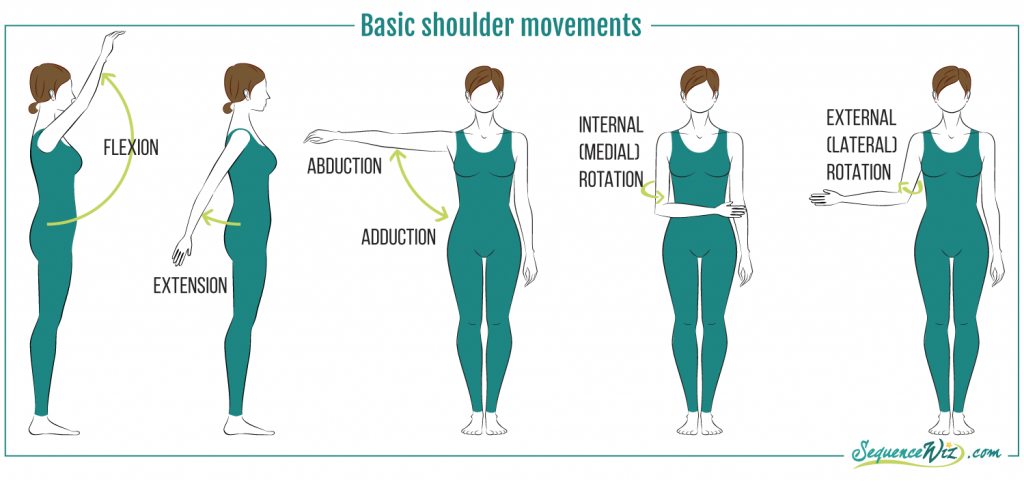
Five types of muscle movements
Adduction – Adduction involves moving a body part toward the mid-line of the body.
Abduction – abduction means moving a body part away from the body.
Flexion – Flexion means bending a joint to decrease the angle between two bones.
Extension – Extension means to extend or straighten a joint to increase the angle between two bones.
Rotation – Rotation involves moving a body part around an axis.
Other structures essential to the muscular system
Tendons – Tendon are tissues that attach muscles to bones. They are remarkably strong with high tensile strength that can be attributed to its constituent collagen (an important protein building block of our body) fibers.
Fascia – Fascia is a soft fibrous tissue that envelopes, separates or binds together muscles, group of muscles, organs and other tissues of the body. Fascia also permits some other muscles to slide smoothly over each other. In simple words, they connect muscles to other muscles.
Coordination with the Nervous System and the Skeletal System –
As discussed earlier the skeletal muscles are controlled by the nervous system. The muscular system uses muscles to move the bones of the skeletal system. However, if the communication between the nervous system and the muscular system gets damaged, then the muscular system will not be able to bring about any movement in the body parts! This causes paralysis.
How do muscles move a bone?
Let’s say you want to pick up a book. In order to lift it, your biceps will have to contract and the triceps will have to lengthen or stretch to make your arm bend at the elbow.
When the muscle relationship is reversed, that is when the biceps relax and the triceps contract, the arm will come back to its original position and you can put the book down.
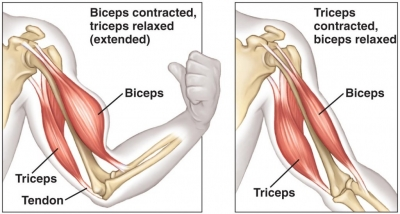
Thus muscles always work in pairs. When one muscle in a pair contracts to bend a joint, its counterpart then contracts and pulls in the opposite direction to straighten the joint out again. The two proteins actin and myosin present in muscle cells help in contraction of muscles by changing the length and shape of the cells.
So now you know why people take protein supplements to build their muscles! Aside from proteins, we also need carbohydrates, healthy fats, plenty of water, Magnesium (it helps in muscle contraction) and regular exercise to aid a healthy and strong Muscular System.
Check point
- The property of a muscle to recoil or bounce back to the muscle’s original length and shape after contraction is called _______.
- The enlargement of muscles due to extra work out is called muscular ________.
- Bending a joint to decrease the angle between two bones is called ______.
- The mineral that is required in our diet for healthy muscles is _______.
- Muscles always work in pairs, when one muscle contracts, the other ________.
Answer Key
- elasticity
- hypertrophy
- flexion
- magnesium
- relaxes
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
Picture credits :
https://www.uc.edu/content/dam/uc/ce/images/OLLI/Page%20Content/Muscular%20System%20s.pdf
https://healthclubfinder.org/gym-workout-schedule-for-men/
http://www.healthfine.org/articles/192245
https://ftiinc.org/why-you-need-to-shred-protein-hot/
https://www.mutantworkout.org/muscles/function-of-smooth-muscle/
https://sequencewiz.org/2016/03/16/loosen-up-your-shoulders/
http://myscienceschool.org/index.php?/archives/1597-How-do-muscles-work.html