Matter and its Structure
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
What is Matter?
Everything around us is Matter – it is the substance of which all things are made. Anything which occupies space is matter – it has a Volume. And it has a certain quantity in every object – called its Mass. So, any substance which has mass and takes up space by having volume is Matter. Our atmosphere, the earth, the Sun, planets, and stars, the animals, trees, and marine life, even our own bodies, all constitute matter.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
What are the Properties of Matter?
How do we recognize the many varieties of matter? Based on their special characteristics, or properties!The matter has physical and chemical properties.
Physical Properties are those which we can recognize by our senses – sight, sound, smell, touch, taste. For example, we recognize gold by its color, sugar by its taste, and gasoline by its smell.
Chemical Properties are based on how one kind of matter acts when it undergoes a chemical change. For example, iron rusts when it comes in contact with moist air – this is a chemical property of iron.
What is Matter made of?
The tiniest bit of all matter is the Atom. The tiniest bit of gold is one atom of gold. The tiniest bit of oxygen, of mercury, indeed of every solid, liquid, and gas in the universe, is one atom of that matter. It is the most basic unit of all matter. All matter is made of atoms.
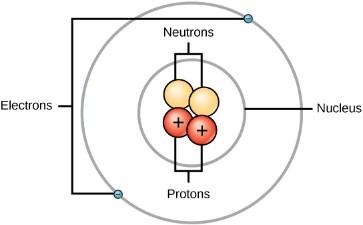
Atoms are made up of even smaller things, called Subatomic Particles! There are three subatomic particles in every atom. All atoms of the same matter (gold or mercury or oxygen) have the same numbers of these subatomic particles. These particles are –
- Protons
- Neutrons
- Electrons
Protons and Neutrons are at the center of the atom, in a space called the Nucleus. Electrons are constantly whizzing around the nucleus in random paths known as Orbits. Even protons and neutrons constantly move at random inside the nucleus.
The quantity of matter in an atom is known as its Mass. The nucleus has almost all of the mass of an atom, meaning that electrons have really very little mass.
What are the Elements?
All atoms of the same kind make up an Element –
- All atoms of oxygen make up the Gaseous Element known as oxygen
- All atoms of gold make up the Solid Element known as gold
- All atoms of mercury make up the Liquid Element known as mercury
So, an elementcan be solid, liquid or gas. An element is the most basic chemical substance. It is a pure substance which cannot be further broken down by any chemical means. In chemical terms, all the atoms of an element have exactly the same number of protons in their nuclei. All the known elements in the universe are arranged in thePeriodic Table.
What are Molecules?
Atoms of the same element, or of different elements, combine to form Molecules –
- Two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule
- Two hydrogen atoms combine to form a hydrogen molecule
- Two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom to form a liquid molecule: water
- Two oxygen atoms combine with one carbon atom to form a gas molecule: carbon dioxide
- One sodium atom combines with one chlorine atom to form a solid molecule: salt
A molecule retains all the properties of the substance from which it is obtained. Further division of a molecule yields only atoms of the individual elements.
What are Compounds?
When atoms of different elements combine chemically in a fixed ratio, the result has named a Compound. In the examples above, water is a compound. So are carbon dioxide and salt. Compounds are only created chemically and can only be separated through chemical means. Each compound has its own unique properties, which are different from the properties of the individual elements from which it is made. Compounds may be solids, liquids, or gases.

What are Mixtures?
If two or more elements or compounds are physically mixed together, the result is a mixture.A mixture is not formed through chemical means. Examples of mixtures are –
- Salt dissolved in water to make saltwater
- Coffee with milk
- Air
- Soil
- Vegetable soup
The components of a mixture can be separated by various physical means without the need for any chemical reaction. For example, saltwater can be separated into salt and water simply through evaporation of the water. A mixture may be Homogenous, meaning that the composition is uniform throughout the mixture, or Heterogenous, meaning that the composition is not uniform. In the examples above, saltwater, coffee with milk, and air, are homogeneous mixtures, while soil and vegetable soup are heterogeneous mixtures.

Check Point
- Which of these are properties of matter?
- Mass
- Volume
- Weight
- Smell
- All of the above
- ______ whiz around the nucleus in fixed orbits.
- All atoms of the same kind make up an ______.
- The division of a molecule yields only ______ of the individual elements.
- Soil is an example of a ______ mixture.
Answer Key
- e) All of the above
- Electrons
- Element
- Atoms
- Heterogenous
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System