Electricity and Magnetism
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
Electricity and Magnetism
It is a phenomenon associated with stationary or moving electric charges. Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter and is borne by elementary particles. In electricity the particle involved is the electron, which carries a charge, as negative. Electricity is not a form of energy. Instead, it is said that an electric current is a flow of “electricity”.

Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Coulomb’s Law
Static electricity is an electric phenomenon in which charged particles are transferred from one body to another.
For example, if two objects are rubbed together, especially if the objects are insulators and the surrounding air is dry, the objects acquire equal and opposite charges and an attractive force develops between them.The object that loses electrons becomes positively charged, and the other becomes negatively charged.
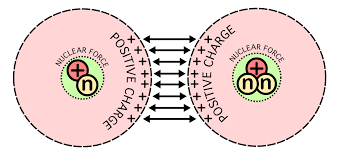
Credit: http://abdullatif-nuclearenergy.blogspot.in/
When one object is rubbed against another, static electricity is created. This is because the rubbing creates a negative charge that is carried by electrons. These electrons build up to produce static electricity.

Credit: http://coolscienceexperimentshq.com/how-to-make-your-hair-stand-on-end/
Some other examples are –
- Rubbing one’s feet on the carpet
- Clothes tumbling in the dryer
Credit: http://www.absorvalia.cat/manteniment/
Learn more about Electricity and Magnetism and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Personalized Online Tutoring from eTutorWorld
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE TRIAL Session.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Magnets and Electricity
In most objects, all the atoms are in balance with half of the electrons rotating in one direction and half rotating in the other direction.
Magnets are quite different with the atoms at one end having electrons spinning in one direction while those at the other end spin in the opposite direction.
We call one end of the magnet the North (N) Pole and the other end the South (S) Pole.
The force of the magnetic field flows from the North Pole to the South Pole. If you hold two magnets close to each other you would find that if you try to push the two North poles (N) or the two South poles (S) together, they repel each other. If you put the North Pole (N) near the South Pole(S), they attract each other.
Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
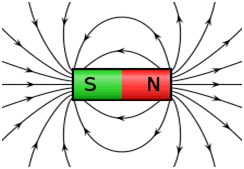
Electricity can make magnets
Each electron is surrounded by a force called an electric field. When an electron moves, it creates a second field – a magnetic field. When electrons are made to flow in a current through a conductor, such as a piece of metal or a coil of wire, the conductor becomes a temporary magnet – an electromagnet.
What is the relationship between electricity and magnetism?
Electric current flowing through the wire produces magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field depends on the direction of electric current. A changing magnetic field produces an electric current in a wire. The relationship between electricity and magnetism is called electromagnetism.
Magnets can make Electricity
A magnetic field pulls and pushes electrons in some objects near them to make them move. For example, in copper metal electrons those are freely movable. When a magnet is swiped along quickly through a copper wire, electrons move and so electricity is made.

When current flows through any wire it creates a magnetic field around the wire as it goes along. Generally it’s quite weak because a single wire is not strong enough to pickup metal objects. Here “I”Is the current and “B” is the magnetic field.

Credit: https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromagnet
Electrostatics, the study of electric charges at rest, was initially found by the ancient Romans who observed how a comb after brushing would attract particles. It is known that electric charges are in two different forms, positive charges and negative charges. Like charges repel each other, and differing charges attract.
The force that attract positive charges to negative charges weakens with distance, but is very strong — up to 40 times stronger than the pull of gravity at the surface of the earth. This fact can easily be described by a small magnet that can hold or suspend an object. The small magnet exerts a force at least equal to the gravitational from the entire Earth.

Credit: https://nameshe.wordpress.com/page/6/
Check Point
A. Fill in the blanks –
- In electricity the particle involved is the ………….. This carries a charge, as negative.
- ………….. electricity is an electric phenomenon in which charged particles are transferred from one body to another.
- The force of the ………….. flows from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- When electrons are made to flow in a current through a conductor, such as a piece of metal or a coil of wire, the conductor becomes a temporary magnet, an …………..
- ………….. the study of electric charges at rest.
B. State True or False –
- Electricity is a form of energy.
- Like poles attract, unlike poles repel
- The force of the magnetic field flows from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- Each electron is surrounded by a force called a magnetic field.
- Electrostatics, the study of electric charges at rest.
Answer Key
A. Fill in the blanks –
- Electron
- Static
- Magnetic field
- Electro magnet
- Electro statistics
B. State True or False –
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
Learn more about Electricity and Magnetism and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Elements & Compounds
- Solar Energy
- Photosynthesis
- Digestive System
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Law of conservation of energy
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Periodic table
- Properties of Matter
- Waves
- Energy Resources
- Weather and Climate
- Immune, Circulatory and Digestive Systems
- Organs in Multi-cellular Organisms
- Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic Rocks
- Structure of the Earth
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Scientific Method
- Cycles in Nature
- Environmental Science
- Renewable and Non-renewable energy Resources
- Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Life Science
- Earth and Space Science
- Solar Eclipse
- Heat Technology
- Newton’s Laws of Motions
- Physical Science
- Tools, Measurement and SI Units
- Earth Atmosphere
- Interactions of Living things
- The Earth Ecosystem
- Organelles in Plant and Animal cells
- Layers of the Earth