Adaptations
Grade 6 Science Worksheets
Habitat
Living creatures are collectively called as organisms. The place where organisms live is called a habitat. Habitat is a home that provides food, water, air, shelter, and other needs to organisms. Several kinds of plants and animals may share the same habitat.
Adaptation
All living organisms have certain features that help them live in the surroundings in which they are normally found. The presence of specific features or certain habits, which enable an organism to live naturally in a place, is called adaptation.
Living organisms are adapted to their environment. This means that the way they look, the way they behave, how they are built, or their way of life makes them suited to survive and reproduce in their habitats.
The types of habitats vary from organism to organism. The plants grow better and survive longer in a particular habitat to which they are adapted.
Habitats can be divided into 3 broad categories:
- Terrestrial Habitats
- Aquatic Habitats
- Aerial Habitats
Some plants prefer to live in hot and dry areas of land – e.g. cactus. Cactus plant grows and survives well in the hot and dry areas of deserts. This is because cactus is adapted to live with very little water for long periods of time. So, cactus is adapted to grow in the desert.
Some plants prefer to live in water e.g. lotus plant grows and lives in the water of a pond. It cannot survive without sufficient water. So, a lotus plant is adapted to grow in water.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Terrestrial Habitats:
The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats. Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, grasslands, wetlands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions.
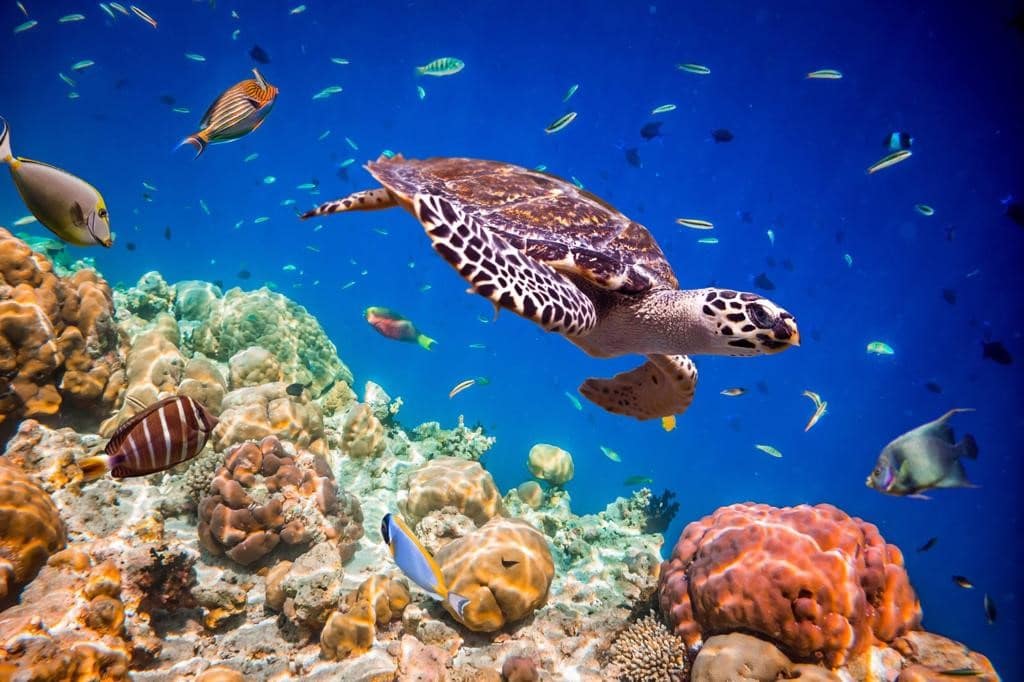


Aquatic Habitats:
The habitat of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats. Lakes, rivers and oceans are some examples of aquatic habitats.
Aerial Habitats:
Organisms that are capable to do their activities in the aerial environment are called as aerial organisms. Some examples of animals found there are birds, bats and some insects. Aerial habitats are in the sky. Example: trees.

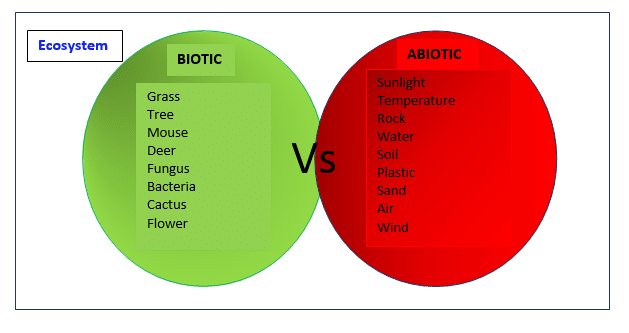
Ecosystems – Biotic and Abiotic Components
Biotic components are the living things that shape an ecosystem. The organisms, both plants and animals living in a habitat are its biotic components. Hence, some of the examples of biotic components are animals, plants, fungi and bacteria.
Abiotic components are non-living components that influence an ecosystem. Examples of abiotic factors are rocks, soil, air, and water.
Hence, ecosystems are influenced by both biotic and abiotic components.
Personalized Online Tutoring from eTutorWorld
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE TRIAL Session.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
A Drive through Different Habitats
Let us see in detail, about the different phenomena of adaptations involved in plants and animals under various habitats.
Terrestrial Habitats:
- Deserts
- Mountain Regions
- Grasslands
Deserts:
Deserts are habitats that have no more than 20 inches of precipitation per year and can be hot or cold. The four types of deserts are hot and dry, semi-arid, coastal, and cold. Desert plants and animals are able to live with little water.
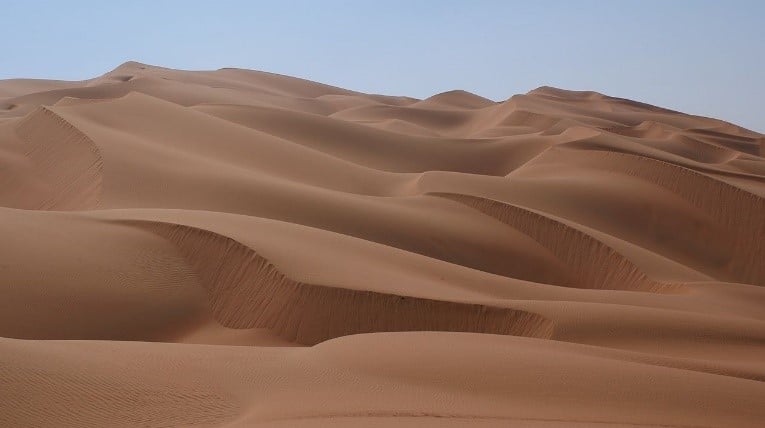


Animal Adaptations in Deserts:
Let us discuss some of the animals found in the desert which are well-adapted to this environment. The most well-known desert animal is the camel. The body structure of a camel helps it to survive in desert conditions. Some of the special features of a camel are:
- A camel’s ears are lined with fur to filter out sand and dust blowing into the ear canal.
- A camel’s eyes are large and are protected by a double row of long curly eyelashes that also help keep out sand and dust, while thick bushy eyebrows shield the eyes from the desert sun.
- Camels have broad, flat, leathery pads with two toes on each foot. When the camel places its foot on the ground the pads spread, preventing the foot from sinking into the sand. When walking, the camel moves both feet on one side of its body, then both feet on the other. This gait suggests the rolling motion of a boat, from which the nickname ‘ship of the desert’ was derived.
- Contrary to popular belief, a camel does not store water in its hump. It is in fact, a mound of fatty tissues from which the animal draws energy when food is hard to find.
- Camels have long legs that help to keep their bodies away from the heat of the sand.
- A camel passes a small amount of urine; its dung is dry and it does not sweat. Since a camel loses very little water from its body, it can live for many days without drinking water.

Desert animals like rats and snakes do not have long legs like a camel. To stay away from the intense heat during the day, they stay in burrows deep in the sand. These animals come out only during the night when it’s cooler.
Plant Adaptations in Deserts:
Desert plants lose very little water through transpiration. The leaves in desert plants are either absent, very small, or they are in the form of spines. This helps in reducing the loss of water from the leaves through transpiration. The leaf-like structure you see in cactus is in fact its stem.
Photosynthesis in these plants is usually carried out by the stems. The stem is also covered with a thick waxy layer, which helps to retain water in the tissues of cacti. Most desert plants have roots that go very deep into the soil for absorbing water.
Some examples of plants that grow in deserts are – Palm trees, Cactus, Desert Marigold etc.

Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Mountain regions:
Mountains can sometimes act like barriers preventing plants and animals from crossing from one side of the mountain to the other.
Different ecosystems exist on each side of a mountain. One can often find different ecosystems as you climb up from base to the peak of a big mountain. Due to the rapid changes in altitude (height) and temperature along a mountain slope, ecosystems can change quickly from one area to another.
Animal Adaptations in Mountain Regions:
These habitats are normally very cold and windy. In some areas, snowfall may take place in winters. There are a large variety of plants and animals living in the mountain regions.
Some examples of animals that are adapted to mountain regions are Snow leopard, Yak and Mountain goat, llama etc.
Snow leopards are very well-adapted to the areas in which they live, which mostly consist of mountains and high rocks. Snow leopards have –
- Deep nasal cavity and a large chest which helps the animal breathe at high altitudes.
- Good eye sight, helping them spot out prey.
- Small ears which can be flattened down to help keep their ears from getting frostbite.
Plant Adaptations in Mountain Regions:
The trees are normally cone shaped and have sloping branches. The leaves of some of these trees are needle-like. This helps the rain water and snow to slide off easily. There could be trees with shapes very different from these that are also present on mountains. They may have different kind of adaptations to survive on the mountains. Some examples of plants/ trees that grow in mountain regions are fir trees, maple, pine trees etc.
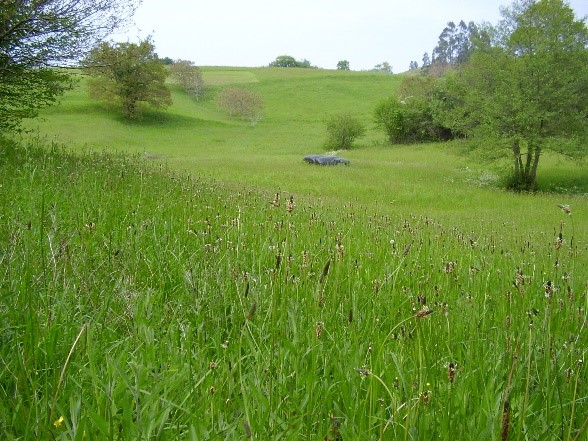

Grasslands:
Grasslands are vast areas of grass stretching off towards the horizon. Grasslands are defined as areas where there is very little rainfall to support a forest, but too much rainfall to classify the land as a dry desert. Trees aren’t common in grasslands, either because of poor soil and lack of overall rainfall or from excessive tree grazing from grassland animals. In Temperate grasslands, rainfall is low throughout the year, with hot summers and cold winters. Tropical grasslands, on the other hand, receive seasonal rainfall and are generally warm throughout the year.
Animal Adaptations in Grasslands:
Tigers:
The tiger’s striped coat helps them blend in well with the sunlight, filtering through the treetops to the jungle floor. The tiger’s seamless camouflage to their surroundings is enhanced because the striping also helps break up their body shape, making them difficult to detect for unsuspecting prey.
Lions:
A lion is a strong animal that can hunt and kill animals like deer. Its light brown color helps it to hide in dry grasslands when it hunts for prey. Lions have long claws in their front legs that can be withdrawn inside the toes. The eyes in front of the face allow it to have correct idea about the location of its prey.
Deer:
The deer has skinny legs for running fast and their tail is for a warning. Whenever the deer thinks there is danger it sticks up its tail and let the other deer know. Deer also have fur to keep them warm in winter. They have antlers and hooves to keep them safe. The eyes on the side of its head allow it to look in all directions for danger.
Plant Adaptations in Grasslands:
There are many more plants that live in the grasslands besides grasses. But all plants in this environment face difficult conditions. It only rains 10-30 inches during the late spring and early summer. There are also lots of plant eating animals, and fires are known to sweep through grasslands, burning many plants at a time.
Grassland plant adaptations include deep roots, narrow leaves and brightly colored flowers. Here, the grasses grow from the base of the plant rather than the tips. This enables them to survive the fires that commonly occur in the dry, hot climate of grasslands.
Aquatic habitats
Oceans:
Fishes and other sea animals have streamlined bodies to help them move easily in water. There are some sea animals like squids and octopuses, which do not have this streamlined shape. They stay deeper in the ocean, near the seabed and catch any prey that moves towards them. However, when they move in water they make their body shapes streamlined. These animals have gills to help them use oxygen dissolved in water.
There are some sea animals like dolphins and whales that do not have gills. They breathe in air through nostrils or blowholes that are located on the upper part of their heads. This allows them to breathe in air when they swim near the surface of water. They can stay inside the water for a long time without breathing. They come out to the surface from time to time, to breathe in air.
Ponds and Lakes:
In aquatic plants, roots are much reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place. The stems of these plants are long, hollow and light. The stems grow up to the surface of water while the leaves and flowers float on the surface of water.
Some aquatic plants are submerged in water. Some of these plants have narrow and thin ribbon-like leaves. These can bend in the flowing water. In some submerged plants, leaves are often highly divided, through which the water can easily flow without damaging them.
Adaptations in Fishes:
About half of the fishes live in freshwater bodies such as lakes and streams while the other half live in the oceans.
Fish show great diversity in body size. They range in length from about 8 millimeters (0.3 inches) to 16 meters (about 53 feet). Scales protect fish from predators and parasites and reduce friction with water. Multiple overlapping scales provide a flexible covering that allow fish to move easily while swimming. Gills present in the fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water.


Adaptations in Frogs:
Frogs usually live in ponds. They can stay both inside the water as well as move on land.
Adaptations of frogs, such as a small waist, no neck and a broad, flat skull make its body streamlined for swimming. The frog’s skin is thin, which allows air to pass through, in effect allowing it to breathe through the skin. Powerful hind legs and feet allow the frog to jump and help them in leaping and catching its prey.
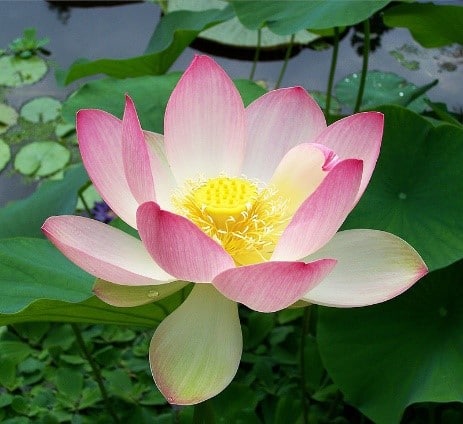
Adaptations in Lotus:
Lotus leaves are wide and disk-shaped, which allows them to float on water. Their big surface area allows them to absorb a large amount of sunlight. Lotus leaf and stem surfaces are coated in a wax that is super-hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and is very difficult to wet. Lotus flowers bloom white, pink and yellow and are held above the water by a stem that is 2 to 4 feet tall. Many birds and insect species feed on lotus pollen. These animals distribute pollen to fertilize neighboring plants and scatter seeds. The adaptation of a brilliant color for the flowers attracts feeders.

Aerial Habitats:
Animals that can fly in the air are called aerial animals. Birds and bats fly in the air. Birds have wings to fly. They also have hollow bones which make their body light and help them fly.
Bats are not birds. They are mammals. They do not have actual wings. Their wings are made of flaps of skin. Many insects also have wings which help them fly in the air.
Human Adaptations
Humans exhibit a number of biological adaptations to the great variety of environments they occupy.
Acclimatization
This form of adaptation can take moments to weeks to occur and is reversible within an individual’s lifetime.
Short-term acclimatization can occur within a short period of time (days to weeks), and within the organism’s life time. This type of response quickly reverses when the stressor is no longer present. Tanning is a short-term response, to increased UV-radiation exposure especially during summer months, which can occur within hours. Tans are generally lost during the winter when UV-radiation decreases.
Developmental acclimatization occurs during an individual’s growth and development. Note that these cannot take place once the individual is fully grown. An example of this is those who have grown up at high altitude vs. those who have moved to high altitude as adults. Those who were born at high altitude tend to develop larger lung capacities than do those who were not born at high altitude, but moved there later in life.
Genetic adaptations:
Body forms that are adapted to climate like in animals are called genetic adaptations.
- Tropical people are generally tall and lean to lose heat.
- Arctic and mountain people are short and wide to conserve heat.
There are two ecological rules, known as Bergmann’s rule and Allen’s rule that explain the variation in size and shape of bodies and extremities using latitude and temperature.
Bergmann’s rule:
Warm-blooded animals tend to have increasing body size with increasing latitude (toward the poles) and decreasing average temperatures.
Allen’s rule:
Warm-blooded animals tend to have shorter limbs with increasing latitude and decreasing average temperatures.
When organisms are more compact, they tend to conserve heat. When organisms are more linear, they tend to lose more heat.
This has been applied to humans. The idea is that populations towards the pole tend to be shorter and have shorter limbs than do people on the equator.
Differing skin colors are simply our bodies’ adaptation to varied climates and levels of UV exposure. Pale skin is adapted to vitamin D photosynthesis in dim climates.
Therefore, adaptations occur as a result of changes in the environment, life style or relationship to other organisms. Different organisms have different adaptations and ability to cope with their environmental problems. They even make a few modifications to their way of life in order to survive. The modifications and adaptations might be either in the way of feeding, breathing or even breeding. They must adapt the changes in order to survive.
Check Point
Fill in the blanks:
- The place where organisms live is called a ______________.
- Deserts are a type of __________ habitat.
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
- Aerial
- Arboreal
- The presence of specific features or certain habits, which enable an organism to live naturally in a place, is called__________________.
- The habitat of plants and animals that live in water are called _____________.
- Which of the following are biotic components?
- Grass
- Tree
- Soil
- Both a & b
- The four types of deserts are hot and dry, semi-arid, _____________ and cold.
- ___________ are vast areas of grass stretching off towards the horizon.
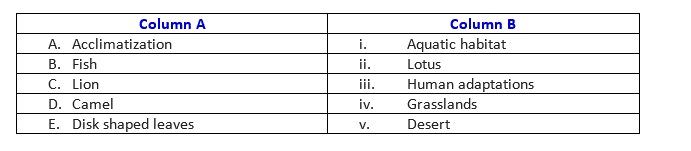
- Match the following:
9. What kind of adaptation does tanning of human skin come under?
- Genetic adaptation
- Short term acclimatization
- Developmental acclimatization
10. Which of the following is NOT a terrestrial habitat?
- Forests
- Wetlands
- Pond
- Coastal regions
Answer Key
- The place where organisms live is called a
- Choice (a) – Deserts area a type of terrestrial habitat.
- The presence of specific features or certain habits, which enable an organism to live naturally in a place, is called
- The habitat of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats.
- Choice d – Both a & b – Both grass and tree belong to biotic components.
- The four types of deserts are hot and dry, semi-arid, coastal and cold.
- Grasslands are vast areas of grass stretching off towards the horizon.
- A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-v, E-ii
- Choice b – Short term acclimatization. Tanning of human skin comes under short term acclimatization.
- Choice c – Pond. Pond is not a terrestrial habitat.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Adaptation
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Evolution
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Astronomy
- Ecology
- Energy
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Sound
- Light
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
Image Credits:
Terrestrial habitats – https://photos.app.goo.gl/VVeh1Yxyna3KfRzs9
Aquatic habitats: https://photos.app.goo.gl/VVeh1Yxyna3KfRzs9
Aerial habitats – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eurasian_Cranes_migrating_to_Meyghan_Salt_Lake.jpg
Deserts – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Rub_al_Khali_002.JPG
Camel – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Camelus_dromedarius_on_Sinai.jpg
Rat – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Kangaroo-rat.jpg
Desert plants – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Various_Cactaceae.jpg
Grasslands – https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Prau.JPG
Fish – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Altolamprologus_compressiceps_-_Karlsruhe_Zoo_01.jpg
Frog – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Litoria_tyleri.jpg
Lotus – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sacred_lotus_Nelumbo_nucifera.jpg