Human Nervous System
Grade 5 Science Worksheets
Suppose you are late for school one day. You see the school bus at a distance and start running towards it. Or if you are cold, would you ask your Mum for a jacket? Did you know that it is the nervous system that tells you to run or ask for that jacket?
The Human Nervous System is a complex system that coordinates all activities of the body and enables the body to respond and adapt to changes that occur both inside and outside of it. The components of the nervous system include a network of nerve cells and fibers that transmit nerve impulses between parts of the body. Nervous systems are found in most multicellular animals but vary in their complexity.
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Nervous System in Humans
The Nervous system in humans helps us to coordinate all our voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical signals to and from different parts of the body. Human beings are blessed with high sensory-motor abilities. The endocrine system (glands and hormones) and muscles work together with the nervous system and influence many aspects of human behavior.

Credit: https://www.armiusa.org/news/2018/8/1/automation-and-the-body-wires-and-networks-vs-nervous-system
Neurons and Glial Cells
The primary components of the Nervous System are known as NEURONS. A human brain contains about 100 billion neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that forms the nervous tissue. It is a special cell that can receive and transmit chemical or electrical signals. It is capable of communicating with other cells by releasing chemicals known as neurotransmitters at specialized junctions known as SYNAPSES. It consists of a cell body, dendrites, and a single axon as shown below.
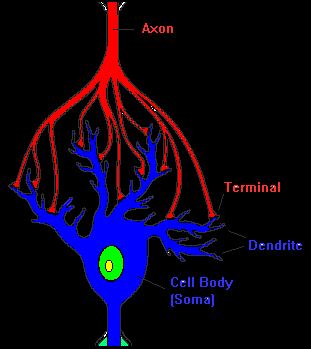
credit: https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/gif/synnew.gif
Synapse
The neurons receive signals via their dendrites and send out signals down the axon. Mostly, signals cross over from the axon of one neuron to a dendrite of the next neuron. The myelin sheath is an insulating layer that aids in quick transfer of electrical impulses.
GLIAL CELLS OR GLIA are the non-neuronal cells in the Nervous System that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection to neurons.

credit: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/neuron-anatomy
Nerve Cell/ Neuron
Learn more about Human Nervous System and other important topics with 5th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Personalized Online Tutoring from eTutorWorld
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE TRIAL Session.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Types of Neurons
There are three major types of neurons. All of them are crucial for the brain to function effectively. They are as follows:
- Sensory Neurons (Afferent neurons) – They carry external stimuli from the organism’s environment towards the central nervous system.
- Motor Neurons (Efferent neurons) – They carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland.
- Relay Neurons (Interneurons) – They are found between the sensory and motor neurons and allow them to communicate.
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensation: The nervous system receives information about the environment around us via a specialized group of cells known as RECEPTORS. Receptors present in our sense organs detect stimuli, like change in temperature, pressure, light, etc. and transmit a signal to a sensory nerve or an afferent nerve.
Integration: The sensory or afferent nerve carries the impulse towards the CNS, where the information is processed to determine an appropriate response.
Response: The brain combines sensory perceptions and higher cognitive functions like memory, learning, and emotion to generate a response. Finally, it sends out the response signal via motor nerves or efferent nerves to muscles, organs, or glands to bring about the requisite action.
These functions are divided between two main parts of our Nervous System:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
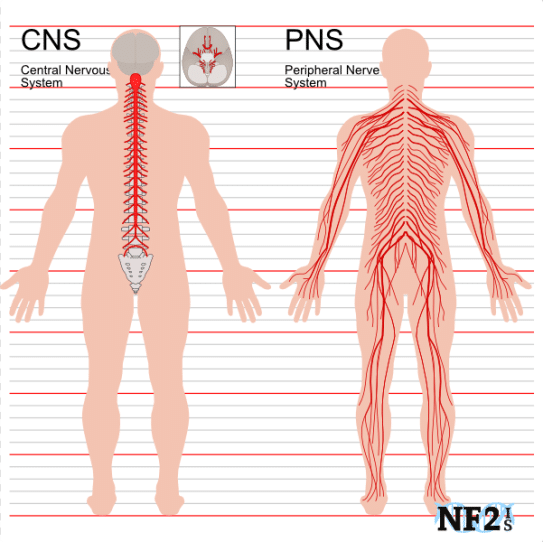
The Central Nervous System
The CNS is a part of the Nervous System that consists of the Brain and the Spinal Cord.
- BRAIN: It integrates sensory information and coordinates body functions, both consciously and unconsciously. Complex functions like homeostasis, emotions, thinking and memory also are attributed to the brain. It also controls basic life functions like breathing and heart rate. The brain is largely divided into cerebrum (frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes), the brainstem, and the cerebellum. Their functions can be divided as follows:

Credit- https://www.humanbrainfacts.org/images/resource/human-brain-functions.jpg
- SPINAL CORD: It serves as a conduit for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It acts as a highway between the body and the brain. It is protected by the vertebrae and consists of nerves that carry incoming and outgoing messages. It also controls reflex actions during emergencies without inputs from the brain.

credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/97/Imgnotra%C3%A7at_arc_reflex_eng.svg
Reflex Action: It is an involuntary, automatic, and quick response to a stimulus that does not need conscious thought. The response is generated by the spinal cord without the impulse reaching the brain.
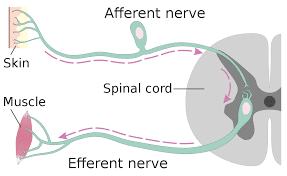
credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Efferent_nerve_fiber
The Peripheral Nervous System
The PNS consists of the nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. Its primary role is to connect the CNS to the body organs, limbs, and skin in order to allow movements and responses to environmental stimuli. It serves as a relay between the brain-spinal cord and the rest of the body. The PNS mainly consists of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers or axons that connect the CNS to every part of the body.
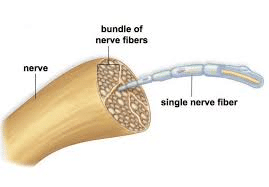
credit: https://microfluidics19.sciencesconf.org/data/pages/Benoit_Charlot_Neurofluidics.pdf
Several Axons make a Nerve
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
The PNS is divided into two parts:
- SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: It controls the voluntary movements of the body with the help of skeletal muscles. It carries nerve impulses back and forth between the CNS and the skeletal muscles, skin, and sensory organs.
- AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: It largely acts unconsciously and regulates bodily functions such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, urination etc. It also controls reflex actions such as sneezing, coughing, swallowing, vomiting among others. Autonomic nervous system has two parts:

Here’s an outline to understand it better:
Now you know that our nervous system constantly works to control and coordinate all our activities inside and outside of our body. So, the next time you see or hear something lovely, remember that the receptors in your eyes or ears are sending impulses to the brain, the brain processes it, and in turn, sends a signal with the help of nerves to the muscles near your lips to bring a smile to your face! Incredible, isn’t it?
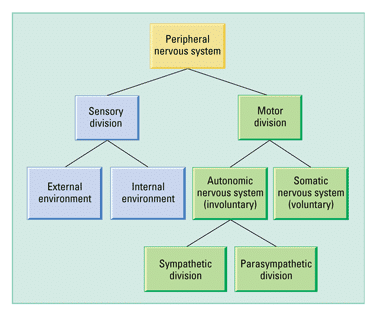
credit: http://bodell.mtchs.org/OnlineBio/BIOCD/text/chapter28/concept28.3.html
Check Point
i.Fill in the blanks:
- The Human Nervous System is divided into __________________ and __________________.
- The nerve cells or nerve fibers are also known as ________________.
- The CNS comprises of ___________________ and ___________________.
- The three types of neurons are ___________, ___________ and ___________.
- The reflex action is a quick reaction to a stimulus that is generated by the ____________.
- In the PNS, the involuntary actions are brought about by Autonomic nervous system and the
voluntary actions are prepared by ______________________.
ii. Label the following:
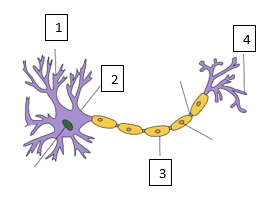
credit:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuron
Answer Key
- Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. They are known as CNS and PNS in short.
- They are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
- The Brain and the spinal cord. They generate and relay responses depending on the stimulus received.
- Sensory, Motor, Relay (also known as afferent, efferent, and interneuron).
- The spinal cord, these actions don’t need conscious decisions and hence, they are quick and used during emergencies.
- Somatic nervous system. They prepare the responses with the help of skeletal muscles.
- 1. Dendrite 2. Cell Body 3. Myelin Sheath 4. Synapse
Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
5th Grade Free Worksheets
- Galaxies
- The Solar System
- Planets
- Structure of Earth
- Plate Tectonics
- Earthquakes
- Volcano and Folded Mountains
- Mountains and Oceans
- Rocks and Fossils
- The Water Cycle
- What Causes Weather Patterns?
- Types of Precipitation
- Climate
- Difference between Weather and Climate
- Impact of Environmental Changes on Humans and Other Organisms
- Plants also Adapt
- Body Systems
- Skeletal System
- Human Nervous System
- Circulatory System
- Respiratory System
- Reproductive System
- Digestive System
- Excretory System
- Atomic Theory
- States of Matter
- Mixtures
- Chemical and Physical Changes
- Types of Energy
- Energy Transformations
- What is Electricity?
- Properties of Electricity
- Uses of Electricity
- Electrical Circuits
- What is Force?
- Newton’s Laws of Motion