Law of Conservation of Mass
Grade 7 Science Worksheets
What is the Principle of Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of mass states that “mass can neither be created nor destroyed”.
Systems can be classified into two categories – Open System and Closed System.
Example: When some hot drink is poured in a mug, the heat escapes within a few minutes and the mug cools down. So, it is an example of open system.

Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Open System
Open System is a system where a quantity can enter or leave the system to a certain degree.
Example: When a liquid is poured in a thermos flask, there is no exchange of heat or matter. So, it an example of closed or isolated system.
The universe is also an example of isolated system.

Closed Sysytem
Closed System is the opposite of an open system. It is a system where quantity cannot enter or leave the system. Closed system is also called as “isolated system”.
Note: Practically, there is no system which is absolutely closed. Closed systems have limited interaction with the environment.
How is the Law of Conservation of Mass shown by a balanced Equation?
In a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants (at the start) = mass of the products (at the end)
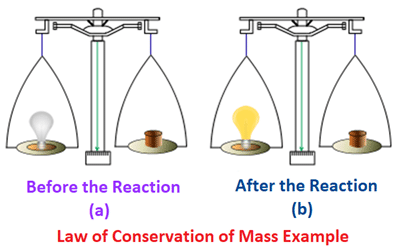
A better glance at the Law of Conservation of Mass
1. Let‘s say A potter uses 150 grams of clay to make a pot.
When you weigh the pot after its done it is equal to 150 grams.
Weight of the clay used to make the pot = weight of the pot.
Hence the law: Mass can never be created nor is it destroyed.
It just changes its form.

Learn more about Law of Conservation of Mass and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Personalized Online Tutoring from eTutorWorld
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE TRIAL Session.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase.
Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
2. Let’s say a cube of ice weighs “x” grams.
When this is weighed after it melts, it weighs the same,
that its weight after melting is “x” grams.
So, weight of the ice cube = weight of the water
Nothing changes with respect to the weight of the ice or water.
It just changes its form.
Mass is neither created not it is destroyed, it’s constant.

3. Experiments involving chemical change also prove the law of conservation of mass.
Weight of (wood + burnt in oxygen) = Weight of the (ashes +carbon dioxide+ water vapor)

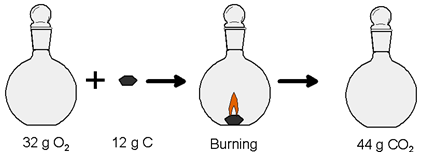
4. How to Prove Law of Conservation of Mass?
Mass of the Reactants = Mass of the Product
Mass of 32 g of oxygen plus 12 g of carbon (before Reaction) = Mass of carbon dioxide (after reaction)
Check Point
A. State True or False
- The law of conservation of mass means, in a closed system, matter cannot be created or destroyed. It changes forms, but is constant.
- Mass of the reactants at the start is always greater than the mass of the product in the end.
- Mass is sometimes viewed as a measure of inertia, the opposition that free bodies offer to forces.
- Matter is always created and destroyed in a closed system.
- The principle of mass conservation, different measurements of the mass of an object taken under various circumstances should always be the same.
B. Explain what does the following mean :
- Mass
- Matter
- Open System
- Closed System
Answer Key
A. True or False:
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
B. Definitions:
- Mass: Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
- Matter: Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
- Open system: a system in which mass or energy can be lost to or gained from its surroundings.
- Closed system: a system in which energy or matter is not exchanged with its surroundings.
Learn more about Scientific Method and other important topics with 7th Grade Science Tutoring at eTutorWorld. Our expert science tutors break down the topics through interactive one-to-one sessions. We also offer the advantage of customized lesson plans, flexible schedules and convenience of learning from home.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $124 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $25 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $239 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $354 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $449 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1049 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2049 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Elements & Compounds
- Solar Energy
- Photosynthesis
- Digestive System
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Law of conservation of energy
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Periodic table
- Properties of Matter
- Waves
- Energy Resources
- Weather and Climate
- Immune, Circulatory and Digestive Systems
- Organs in Multi-cellular Organisms
- Sedimentary, Igneous, and Metamorphic Rocks
- Structure of the Earth
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Scientific Method
- Cycles in Nature
- Environmental Science
- Renewable and Non-renewable energy Resources
- Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Life Science
- Earth and Space Science
- Solar Eclipse
- Heat Technology
- Newton’s Laws of Motions
- Physical Science
- Tools, Measurement and SI Units
- Earth Atmosphere
- Interactions of Living things
- The Earth Ecosystem
- Organelles in Plant and Animal cells
- Layers of the Earth